Introduction
Good gut health is crucial for overall well-being, as it plays a significant role in various aspects of our health, including digestion, immune function, and even mental health. The Gut and Psychology Syndrome (GAPS) diet is a dietary approach that aims to improve gut health and has gained popularity in recent years. In this blog post, we will delve into the GAPS diet and its impact on gut health, exploring the gut-brain connection, the principles of the GAPS diet, success stories, implementation tips, and strategies to optimize gut health alongside the GAPS diet.
Understanding the Gut-Brain Connection
The gut-brain axis is a complex communication network between the gut and the brain. The gut is often referred to as the “second brain” due to its extensive nervous system, and it communicates with the brain through various pathways, including the nervous system, immune system, and hormonal system. Research has shown that the gut and brain are intricately connected, and imbalances in the gut can impact mental health conditions such as anxiety, depression, and autism spectrum disorder.
The GAPS diet recognizes the importance of the gut-brain connection and aims to support gut health to improve overall well-being. By healing and sealing the gut lining, restoring the gut microbiome, reducing inflammation, and improving digestion, the GAPS diet can positively impact the gut-brain axis and support optimal gut health.
What is the GAPS Diet?
The GAPS diet was developed by Dr. Natasha Campbell-McBride, a neurologist and nutritionist, to address gut health issues. It is a therapeutic diet that focuses on removing certain foods that may be contributing to gut issues and incorporating nutrient-dense, healing foods.
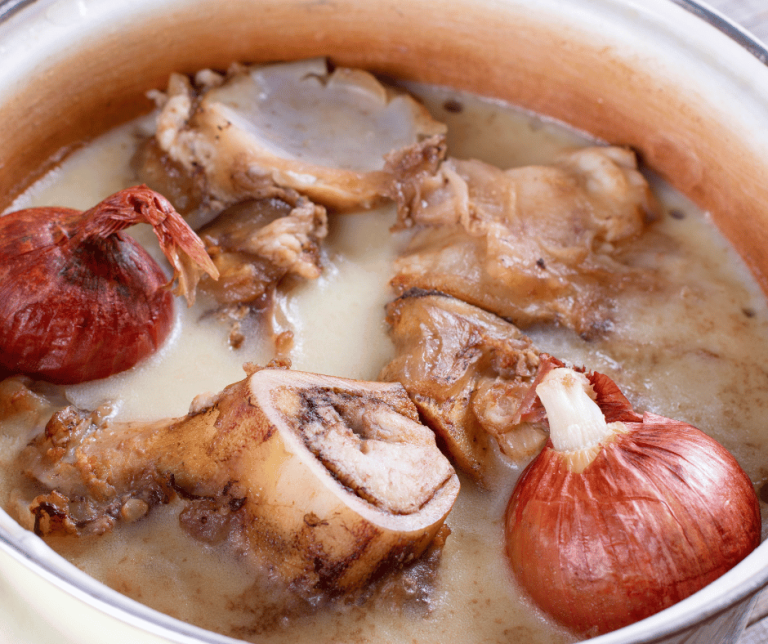
The principles of the GAPS diet include removing grains, processed foods, refined sugars, and other potential gut irritants, and incorporating nutrient-rich whole foods such as organic vegetables, fermented foods, healthy fats, and bone broth. The diet is typically implemented in stages, starting with a strict elimination phase and gradually reintroducing foods based on individual tolerance.
Benefits of the GAPS Diet for Gut Health
The GAPS diet offers several benefits for gut health, including:
Healing and sealing the gut lining: The GAPS diet emphasizes nutrient-dense foods that can help heal and seal the gut lining, reducing gut permeability or “leaky gut syndrome”. This can prevent the passage of harmful substances into the bloodstream and reduce inflammation in the gut.
Restoring the gut microbiome: The GAPS diet encourages the consumption of fermented foods, which are rich in beneficial probiotics that can restore the balance of gut bacteria. This can support a healthy gut microbiome, which is essential for optimal gut health.
Reducing inflammation in the gut: The elimination of processed foods, refined sugars, and other potential gut irritants in the GAPS diet can help reduce inflammation in the gut, allowing the gut to heal and function optimally.
Improving digestion and nutrient absorption: The nutrient-dense foods in the GAPS diet can support proper digestion and nutrient absorption, which is crucial for overall health and well-being.
Conditions That Can Benefit from the GAPS Diet
The GAPS diet has been shown to benefit several health conditions that are associated with gut health issues, including:
Leaky gut syndrome: The GAPS diet’s focus on healing and sealing the gut lining can be particularly beneficial for individuals suffering from leaky gut syndrome, a condition in which the gut lining becomes permeable, allowing harmful substances to leak into the bloodstream and trigger inflammation.
Autoimmune diseases: The GAPS diet’s anti-inflammatory properties and gut healing effects may also be beneficial for individuals with autoimmune diseases, such as Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, and rheumatoid arthritis, as these conditions are often linked to gut health imbalances.
Digestive disorders: Individuals with digestive disorders such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), bloating, constipation, or diarrhea may find relief with the GAPS diet, as it focuses on eliminating potential gut irritants and promoting optimal digestion.
Neurodevelopmental disorders: The gut-brain connection is increasingly being recognized as a contributing factor in neurodevelopmental disorders such as autism spectrum disorder (ASD), attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and learning disabilities. The GAPS diet’s emphasis on gut healing and improving gut health may have positive effects on these conditions.
Success Stories with the GAPS Diet
There are numerous success stories of individuals who have experienced significant improvements in their gut health and overall well-being with the GAPS diet. These success stories often highlight the healing effects of the diet on gut issues such as leaky gut syndrome, digestive disorders, and autoimmune diseases. Personal anecdotes and testimonials can provide inspiration and motivation for individuals considering implementing the GAPS diet as part of their gut health journey.
Implementing the GAPS Diet: Tips and Strategies:
Implementing the GAPS diet may require careful planning and preparation. Here are some practical tips and strategies to help you get started:
Educate yourself: Familiarize yourself with the principles of the GAPS diet and its stages. Understand the foods to eliminate and incorporate, and the potential benefits for gut health.
Seek professional guidance: Consult with a qualified healthcare provider or a registered dietitian who is familiar with the GAPS diet to tailor it to your individual needs and health condition.
Plan meals and stock up on necessary foods: Plan your meals ahead of time and stock up on nutrient-dense foods such as organic vegetables, fermented foods, healthy fats, and bone broth to support the GAPS diet.
Gradual implementation: Start with the elimination phase of the GAPS diet and gradually reintroduce foods based on your individual tolerance. Monitor your symptoms and adjust your diet accordingly.
Incorporate gut-supportive supplements: Probiotics, digestive enzymes, and other gut-supportive supplements may be beneficial in conjunction with the GAPS diet. Consult with a healthcare provider for personalized recommendations.
Practice self-care: Managing stress, getting enough sleep, and staying physically active are crucial for overall gut health. Incorporate self-care practices into your daily routine to support your gut health journey.
Conclusion
The GAPS diet is a therapeutic dietary approach that focuses on improving gut health, and it has shown promising results in supporting individuals with gut-related health issues. By healing and sealing the gut lining, restoring the gut microbiome, reducing inflammation, and improving digestion, the GAPS diet can positively impact overall well-being. However, it’s important to consult with a qualified healthcare provider before implementing any dietary changes, especially if you have a pre-existing health condition. With careful planning, preparation, and personalized guidance, the GAPS diet can be a valuable tool in optimizing gut health and promoting overall wellness. Take a step towards better gut health today with the GAPS diet!
Share this with your friends