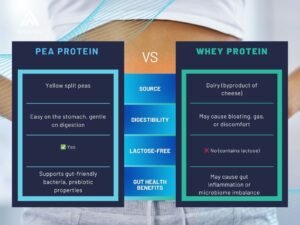
Pea Protein vs. Whey: Which Is Better for Your Gut?
Struggling with bloating after protein shakes? Your choice of protein could be affecting your gut health. Pea protein is gentle and gut-friendly, while whey protein

Home » Unveiling the Power of Probiotics: A Comprehensive Guide to Their Benefits
In a world where the quest for optimal health takes center stage, the spotlight is increasingly turning towards the microscopic inhabitants of our gut—probiotics. These tiny, beneficial microorganisms have been gaining recognition for their remarkable impact on overall well-being. As we delve into the intricate world of probiotics, it becomes essential to unravel their significance, explore their roots, and understand why maintaining a harmonious balance within our gut microbiome is pivotal for health.
Probiotics, derived from the Greek words “pro” (meaning promoting) and “biotic” (pertaining to life), are living microorganisms that confer health benefits when consumed in adequate amounts. The majority of these microorganisms are bacteria, and they play a crucial role in maintaining the delicate balance of our internal ecosystem.
The journey of probiotics traces back centuries, with historical anecdotes hinting at the use of fermented foods for health purposes. However, the term “probiotics” gained prominence in the early 20th century when Nobel laureate Elie Metchnikoff proposed the idea that consuming live microorganisms could have positive effects on health. Since then, research has burgeoned, uncovering the multifaceted benefits of these microscopic allies.
Our gut is a complex and bustling ecosystem, home to trillions of microorganisms that form a diverse community. This gut microbiome plays a pivotal role in various physiological functions, from digesting food to influencing the immune system. Probiotics contribute to maintaining this intricate balance, ensuring that the symbiotic relationship between our body and these microorganisms remains harmonious.
As we embark on this exploration of probiotics and their benefits, it’s crucial to recognize their integral role in fostering a healthy and resilient foundation for our overall well-being. Join us on this journey as we uncover the mysteries and marvels of probiotics.
Now that we’ve established the essence of probiotics, it’s time to dive deeper into the different types and sources of these microorganisms that wield a significant influence on our health.
Lactobacillus Species:
Bifidobacterium Species:
Fermented Foods:
Probiotic Supplements:
Understanding the different types and sources of probiotics is a crucial step towards harnessing their benefits. Whether you choose to indulge in probiotic-rich foods or opt for supplements, incorporating these microorganisms into your lifestyle can contribute to a flourishing gut microbiome. As we proceed, we’ll unravel the profound impact probiotics have on gut health, immune function, and beyond.

As we venture further into the realm of probiotics, it becomes imperative to grasp their integral role in maintaining the delicate equilibrium within our gut microbiome. Let’s explore how these microorganisms actively contribute to promoting gut health and address various digestive concerns.
The gut microbiome is a bustling community of diverse microorganisms, including bacteria, fungi, and viruses. Probiotics, particularly strains of Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, act as the guardians of this microbial community. By outcompeting harmful bacteria and promoting the growth of beneficial ones, probiotics help preserve the balance that is crucial for optimal digestive function.
Probiotics play a pivotal role in breaking down complex carbohydrates, enhancing the absorption of essential nutrients in the intestines. They produce enzymes that assist in the digestion of food, ensuring that nutrients are readily available for absorption. This not only supports overall health but also contributes to increased energy levels and vitality.
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS):
Inflammatory Bowel Diseases (IBD):
Understanding the intricate dance between probiotics and gut health provides valuable insights into the mechanisms behind their digestive benefits. In the next section, we’ll explore how probiotics extend their influence beyond the gut, actively participating in supporting the immune system.

The relationship between probiotics and the immune system is a fascinating interplay that significantly influences our body’s ability to fend off infections and maintain overall health. In this section, we’ll unravel the ways in which probiotics contribute to bolstering the immune response.
Probiotics act as modulators of the immune system, fine-tuning its activity to respond effectively to threats while avoiding unnecessary inflammation. These microorganisms stimulate the production of immune cells and enhance their activity, creating a more robust defense against pathogens.
Respiratory Infections:
Gastrointestinal Infections:
Research suggests that early exposure to probiotics may influence the development of the immune system and potentially reduce the risk of allergic conditions. Probiotics may modulate the immune response, helping to prevent or alleviate allergic reactions in susceptible individuals.
Understanding the immunomodulatory effects of probiotics opens a new dimension to their overall health benefits. As we explore further, we’ll uncover the potential impact of probiotics on mental health and their role in fostering a holistic approach to well-being.
The intricate connection between the gut and the brain, often referred to as the “gut-brain axis,” has gained prominence in recent years. Probiotics, with their profound influence on the gut microbiome, emerge as key players in this dynamic relationship. In this section, we’ll explore how probiotics may impact mental health and contribute to emotional well-being.
Communication Pathways:
Neurotransmitter Production:
Anxiety:
Depression:
Understanding the role of probiotics in mental health adds a layer of complexity to their overall impact on well-being. As we move forward, we’ll explore how probiotics extend their benefits to women’s health, addressing specific concerns related to urogenital health and pregnancy.

While the benefits of probiotics span across various aspects of health, they hold particular significance in supporting women’s well-being. In this section, we’ll delve into the role of probiotics in maintaining urogenital health, preventing infections, and contributing to a healthy pregnancy.
Vaginal Microbiota:
Preventing Yeast Infections:
Supporting a Balanced Microbiome:
Reducing the Risk of Gestational Conditions:
Understanding the specific impact of probiotics on women’s health opens avenues for targeted interventions that can positively influence urogenital health and pregnancy outcomes. As we continue our exploration, we’ll unravel the connection between probiotics and weight management, shedding light on their potential role in supporting metabolic health.
In the pursuit of holistic health, the influence of probiotics on weight management has emerged as a subject of considerable interest. This section delves into how these beneficial microorganisms may play a role in metabolism, weight loss efforts, and the overall maintenance of a healthy body composition.
Regulating Metabolic Processes:
Production of Short-Chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs):
Modulating Gut Microbiota Composition:
Supporting Weight Loss Efforts:
Understanding the intricate connection between probiotics and metabolic processes offers valuable insights for those seeking to maintain a healthy weight. As we progress, we’ll delve into practical tips for seamlessly incorporating probiotics into your daily routine, ensuring a balanced approach to gut health and overall well-being.
As we’ve explored the myriad benefits of probiotics, the next step is to seamlessly integrate these microorganisms into your daily life. Whether through dietary choices or supplements, adopting a proactive approach to nurturing your gut health can have lasting positive effects. Here are practical tips to help you incorporate probiotics into your lifestyle:
Strain Specificity:
Colony-Forming Units (CFUs):
Storage and Shelf Life:
Yogurt and Fermented Dairy Products:
Sauerkraut and Kimchi:
Miso and Tempeh:
Diverse Fiber Intake:
Resistant Starches:
By incorporating these tips into your daily routine, you can create a nourishing environment for probiotics to thrive. Whether through thoughtfully chosen supplements or a diet rich in probiotic foods, fostering a balanced gut microbiome contributes to overall health and well-being. In the following section, we’ll address potential side effects and precautions associated with probiotic consumption, ensuring a well-rounded understanding of their role in health management.

While probiotics offer numerous health benefits, it’s essential to approach their incorporation into your routine with awareness and care. Understanding potential side effects and taking necessary precautions ensures a safe and effective experience with probiotics.
Dairy-Based Probiotics:
Allergic Reactions:
Immunocompromised Individuals:
Antibiotics:
Chronic Health Conditions:
Individualized Recommendations:
Monitoring for Adverse Effects:
Approaching probiotics with caution and mindfulness ensures a positive experience, minimizing potential risks and maximizing the benefits for your health. In the concluding section, we’ll recap the multifaceted benefits of probiotics and highlight their role in fostering a proactive and balanced approach to overall well-being.
As we conclude our exploration into the world of probiotics, it becomes evident that these tiny microorganisms wield a profound impact on various facets of our health. From supporting gut health and bolstering the immune system to influencing mental well-being and contributing to women’s health, the benefits of probiotics are far-reaching.
In our journey through this comprehensive guide, we’ve uncovered the importance of maintaining a balanced gut microbiome and how probiotics play a crucial role in achieving this equilibrium. By understanding the diverse types of probiotics, their sources, and their specific contributions to different aspects of health, you’re equipped with knowledge to make informed choices for your well-being.
Whether you choose to incorporate probiotic-rich foods into your diet, opt for supplements, or consider the synergistic role of prebiotics, the key lies in fostering a harmonious relationship with your gut microbiome. As we’ve explored practical tips for seamlessly integrating probiotics into your lifestyle, it’s essential to do so with an awareness of potential side effects and precautions, ensuring a safe and beneficial experience.
In the dynamic landscape of health and wellness, probiotics stand as allies in our quest for vitality. Yet, it’s crucial to recognize that individual responses may vary, and consulting with a healthcare professional allows for tailored recommendations aligned with your unique health goals and conditions.
In embracing the multifaceted benefits of probiotics, you embark on a journey towards proactive health management. As research continues to unravel the intricacies of the gut microbiome, the future promises further insights into how we can optimize our well-being through these microbial allies.
Here’s to a balanced gut, a resilient immune system, and a thriving well-being – may probiotics continue to play a central role in your journey to optimal health.

Struggling with bloating after protein shakes? Your choice of protein could be affecting your gut health. Pea protein is gentle and gut-friendly, while whey protein

Table of Contents <svg aria-hidden=”true” viewBox=”0 0 448 512″ xmlns=”http://www.w3.org/2000/svg”><path d=”M207.029 381.476L12.686 187.132c-9.373-9.373-9.373-24.569 0-33.941l22.667-22.667c9.357-9.357 24.522-9.375 33.901-.04L224 284.505l154.745-154.021c9.379-9.335 24.544-9.317 33.901.04l22.667 22.667c9.373 9.373 9.373 24.569 0 33.941L240.971

Ever wondered why pooping sometimes feels like a struggle? The way you sit on the toilet could be the problem! Squatting for better pooping is

Feeling backed up in the summer heat? Your gut’s not broken—it’s dehydrated. Discover the powerful, poop-friendly smoothie that combines tropical fruits, digestive enzymes, and hydration

Happy Poops.
What about your friends?