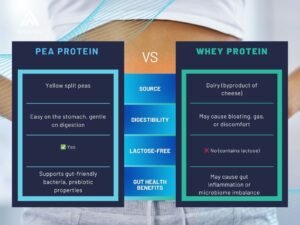
Pea Protein vs. Whey: Which Is Better for Your Gut?
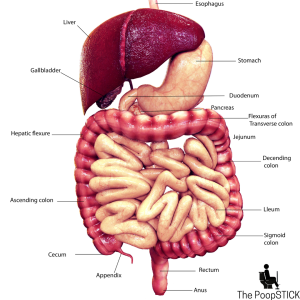
Struggling with bloating after protein shakes? Your choice of protein could be affecting your gut health. Pea protein is gentle and gut-friendly, while whey protein may trigger digestive discomfort. In this post, we compare pea protein vs. whey protein for gut health, breaking down their benefits, drawbacks, and which one is best for you. Keep reading to find out which protein supports digestion and keeps your gut happy!