How Your Diet Shapes Your Bowel Movements (and Gut Health)
What you eat directly impacts your digestion, bowel movements, and overall gut health. Struggling with constipation, bloating, or irregularity? The key lies in your diet.

Home » Gut Health and Nutrient Absorption: Maximizing the Benefits of Your Diet
Gut health is a topic that has gained increasing attention in recent years, and for good reason. The gut, often referred to as the “second brain,” plays a crucial role in maintaining overall well-being. It encompasses a complex ecosystem of microorganisms, enzymes, and tissues working in harmony to digest food, absorb nutrients, and support various bodily functions.
A. Definition of Gut Health
At its core, gut health refers to the optimal functioning of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. This includes the stomach, small and large intestines, and the myriad of microorganisms that inhabit this system. Achieving and maintaining gut health involves a delicate balance of factors, from the types of foods we consume to lifestyle choices and the avoidance of harmful substances.
B. Importance of Nutrient Absorption
Nutrient absorption is a key component of gut health. It’s not just about the quantity of nutrients in the food we eat but also about how effectively our bodies can extract and utilize those nutrients. The digestive process is intricate, involving the breakdown of food into smaller components that can be absorbed by the intestines and transported to various cells and tissues.
C. Connection between Gut Health and Nutrient Absorption
The link between gut health and nutrient absorption is profound. A healthy gut contributes to efficient digestion and absorption of essential nutrients, such as vitamins, minerals, and macronutrients. Conversely, an imbalance in the gut microbiome or disruptions in the digestive process can lead to nutrient deficiencies, impacting overall health and potentially contributing to a range of health issues.
Understanding the intricate relationship between gut health and nutrient absorption is essential for individuals seeking to optimize their diets and enhance their overall well-being. In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the components of gut health, explore the role of the gut microbiome, examine factors that influence gut health, and discuss practical strategies for improving both gut health and nutrient absorption. Through this exploration, we aim to empower readers with the knowledge needed to make informed choices for a healthier, more vibrant life.
A. Overview of the Gut Microbiome
The gut microbiome is a dynamic and diverse community of microorganisms that inhabit the digestive tract, consisting of bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other microbes. This intricate ecosystem, often referred to as the “forgotten organ,” plays a pivotal role in maintaining overall health and well-being. Comprising trillions of microorganisms, the gut microbiome is unique to each individual, influenced by genetics, environment, and lifestyle factors.
The gut microbiome starts developing at birth, influenced by factors such as the mode of delivery (vaginal birth or cesarean section) and early exposure to maternal and environmental microbes. Throughout life, various factors, including diet, medications, and stress, continue to shape and modify the composition of the gut microbiome.
B. Role of Gut Microorganisms in Digestion
The gut microbiome is not a passive bystander in the digestive process; rather, it actively participates in the breakdown of complex carbohydrates, the fermentation of fibers, and the synthesis of certain vitamins. Beneficial bacteria in the gut contribute to the production of short-chain fatty acids, which play a crucial role in maintaining the health of the intestinal lining.
Moreover, the gut microbiome supports the immune system, acting as a barrier against harmful pathogens and aiding in the development of a robust immune response. This symbiotic relationship between the host and gut microorganisms is fundamental to maintaining a healthy gut environment and, consequently, facilitating optimal nutrient absorption.
C. Impact of Microbiome on Nutrient Absorption
The composition of the gut microbiome has a direct impact on nutrient absorption. Some microbes aid in the digestion of dietary fibers, breaking them down into substances that can be absorbed and utilized by the body. Additionally, certain bacteria contribute to the synthesis of vitamins, such as B vitamins and vitamin K, further enhancing the nutritional profile of our diets.
Conversely, an imbalance in the gut microbiome, known as dysbiosis, can lead to digestive issues and compromised nutrient absorption. Conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) are often associated with alterations in the gut microbiome, highlighting the intricate connection between gut health and the ability to absorb essential nutrients.
Understanding the role of the gut microbiome provides valuable insights into how the choices we make, including our diet and lifestyle, can influence this dynamic ecosystem. In the subsequent sections, we will explore the factors that influence gut health, delve into signs of poor gut health, and discuss practical strategies for improving both gut health and nutrient absorption. By doing so, we can unravel the secrets to unlocking the full potential of our digestive system and promoting optimal well-being.
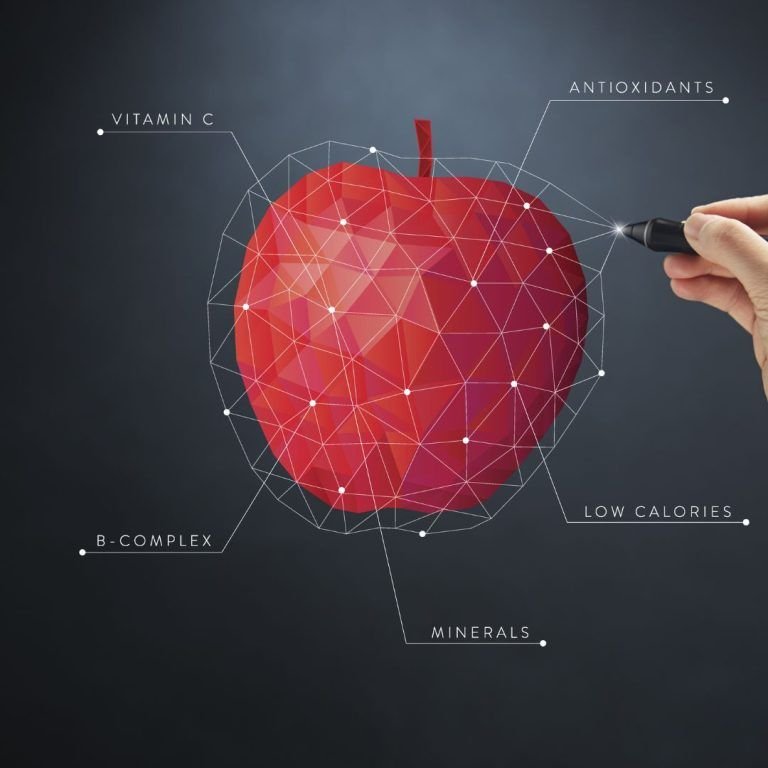
A. Diet and Nutrition
Importance of a Balanced Diet: Achieving and maintaining gut health begins with the food we consume. A balanced diet rich in diverse nutrients provides the necessary building blocks for a healthy gut. Including a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats ensures a broad spectrum of nutrients that support both the gut microbiome and overall digestive function.
Role of Fiber, Probiotics, and Prebiotics: Fiber serves as a crucial component for gut health, promoting regular bowel movements and providing a substrate for beneficial bacteria in the colon. Probiotics, found in fermented foods like yogurt and kimchi, introduce live beneficial bacteria into the gut. Prebiotics, on the other hand, are non-digestible fibers that nourish existing beneficial bacteria. Together, fiber, probiotics, and prebiotics foster a balanced and thriving gut microbiome.
B. Lifestyle Choices
Exercise and Its Effect on Gut Health: Regular physical activity not only supports overall health but also positively influences gut health. Exercise has been shown to promote microbial diversity in the gut, contributing to a more resilient and adaptable microbiome. Incorporating both aerobic and resistance exercises can be beneficial for maintaining a healthy gut environment.
Stress Management: Chronic stress can have detrimental effects on gut health. The gut and brain communicate bidirectionally through the gut-brain axis, and stress can disrupt this communication, impacting digestion and contributing to inflammation. Implementing stress-reducing practices such as mindfulness, meditation, or yoga can play a pivotal role in supporting gut health.
C. Avoidance of Harmful Substances
Impact of Antibiotics: While antibiotics are essential for treating bacterial infections, their use can also disrupt the balance of the gut microbiome by indiscriminately targeting both harmful and beneficial bacteria. Whenever antibiotics are prescribed, it is crucial to follow healthcare professionals’ guidance and consider probiotic supplementation to help restore microbial balance.
Limiting Processed Foods and Artificial Additives: Highly processed foods often contain additives and preservatives that may negatively impact gut health. These additives can alter the composition of the gut microbiome and contribute to inflammation. Choosing whole, unprocessed foods and reading labels to avoid unnecessary additives supports a healthier gut environment.
Understanding the multifaceted factors that influence gut health empowers individuals to make informed choices that positively impact their overall well-being. In the following sections, we will explore signs of poor gut health, strategies for improvement, and the intricacies of maximizing nutrient absorption. By adopting a holistic approach that considers both dietary and lifestyle factors, individuals can cultivate a resilient and thriving gut environment.

A. Digestive Issues
Bloating and Gas: Persistent bloating and excessive gas can be indicative of imbalances in the gut microbiome or difficulties in the digestive process. These symptoms may arise from the fermentation of undigested food by bacteria in the colon, highlighting the importance of efficient digestion.
Irregular Bowel Movements: Consistency in bowel movements is a key indicator of gut health. Diarrhea, constipation, or alternating between the two may signal disruptions in the digestive process, nutrient absorption issues, or imbalances in the gut microbiome.
Abdominal Discomfort: Unexplained abdominal discomfort, pain, or cramping may be associated with inflammation or irritation in the gastrointestinal tract. Identifying the root cause of such discomfort is crucial for addressing underlying gut health issues.
B. Nutrient Deficiencies
Low Energy Levels: Inadequate nutrient absorption can lead to low energy levels, as essential vitamins and minerals play a vital role in energy metabolism. Persistent fatigue without an apparent cause may warrant investigation into potential nutrient deficiencies.
Brittle Nails and Hair Loss: The health of hair and nails can be reflective of overall nutrient status. Deficiencies in key nutrients, such as biotin, zinc, and iron, can manifest as brittle nails or excessive hair loss.
Skin Issues: Skin conditions, including acne, eczema, or psoriasis, may be linked to poor gut health. The gut-skin axis highlights the interconnectedness of these two systems, emphasizing that a healthy gut contributes to radiant and clear skin.
C. Impact on Overall Well-being
Mood Swings and Mental Health: The gut-brain axis establishes a strong connection between gut health and mental well-being. Imbalances in the gut microbiome can contribute to mood swings, anxiety, or even depression. Understanding and addressing the role of the gut in mental health is a crucial aspect of overall well-being.
Weakened Immune System: The majority of the immune system resides in the gut-associated lymphoid tissue. Poor gut health can compromise immune function, leading to increased susceptibility to infections and other immune-related issues.
Recognizing these signs of poor gut health serves as a crucial first step toward implementing positive changes. In the upcoming sections, we will explore effective strategies for improving gut health, emphasizing dietary and lifestyle modifications that support a balanced gut microbiome and enhance nutrient absorption. By addressing these signs, individuals can take proactive steps to optimize their gut health and, in turn, positively impact their overall health and vitality.

A. Dietary Recommendations
Incorporating Fiber-Rich Foods: Including a variety of fiber-rich foods in your diet supports gut health by promoting regular bowel movements and providing a substrate for beneficial bacteria. Whole grains, fruits, vegetables, legumes, and nuts are excellent sources of dietary fiber.
Including Probiotic and Prebiotic Foods: Probiotics introduce beneficial bacteria into the gut, while prebiotics nourish existing microbes. Incorporate fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi for probiotics. Ensure a diet rich in prebiotic fibers by consuming foods like garlic, onions, bananas, and asparagus.
B. Lifestyle Changes
Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity has been linked to a more diverse and resilient gut microbiome. Aim for a combination of aerobic exercises like walking or jogging and resistance training to support overall gut health.
Stress Reduction Techniques: Implement stress-reducing practices such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or yoga to mitigate the impact of chronic stress on the gut. These techniques contribute to a balanced gut-brain axis, fostering a healthier gut environment.
C. Importance of Hydration
D. Nutrient Synergy in Foods
E. Cooking and Food Preparation Methods
F. Timing of Meals for Optimal Absorption
By implementing these strategies, individuals can take proactive steps to improve their gut health and enhance nutrient absorption. Recognizing the interconnectedness of dietary choices, lifestyle habits, and gut well-being empowers individuals to make informed decisions that contribute to a resilient and thriving gut environment. In the final sections, we will dispel common misconceptions about gut health and provide a comprehensive conclusion, summarizing key insights for readers to integrate into their health and wellness journeys.
A. Nutrient Synergy in Foods
Diverse Food Combinations: Consuming a variety of foods in each meal promotes nutrient synergy, where different nutrients work together for optimal absorption. For example, pairing vitamin C-rich foods with iron-rich foods enhances the absorption of non-heme iron, commonly found in plant-based sources.
Balancing Macronutrients: Including a balance of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats in meals supports the absorption of specific nutrients. Fat-soluble vitamins like A, D, E, and K require dietary fats for absorption, emphasizing the importance of incorporating healthy fats such as olive oil, avocados, and nuts.
B. Cooking and Food Preparation Methods
Preserving Nutrient Integrity: Choose cooking methods that preserve the nutritional integrity of foods. Steaming, microwaving, and blanching are cooking techniques that minimize nutrient loss, ensuring that the vitamins and minerals in your food remain intact and bioavailable.
Avoiding Overcooking: Overcooking can lead to the degradation of heat-sensitive nutrients. Keep cooking times to a minimum and avoid boiling vegetables for extended periods, as this can result in nutrient leaching into the cooking water.
C. Timing of Meals for Optimal Absorption
Preventing Nutrient Competition: Some nutrients may compete for absorption when consumed simultaneously. For example, calcium and iron absorption may be hindered when consumed together. Separating the intake of conflicting nutrients or pairing them strategically can help mitigate this competition.
Post-Exercise Nutrient Intake: Timing meals and nutrient intake around exercise can enhance nutrient absorption. Consuming a well-balanced meal that includes carbohydrates and proteins after exercise supports glycogen replenishment and muscle protein synthesis, optimizing nutrient utilization.
Understanding how nutrient synergy, cooking methods, and meal timing influence absorption allows individuals to fine-tune their dietary practices for maximum nutritional benefit. By adopting these practices, individuals can optimize their nutrient absorption, ensuring that the body efficiently utilizes the diverse array of vitamins, minerals, and macronutrients essential for overall health.
In the final sections, we will address common misconceptions about gut health, providing clarity on popular beliefs and emphasizing the importance of a holistic approach to health. The cumulative insights from each section will empower readers to make informed choices that contribute to a balanced gut and, consequently, a healthier and more vibrant life.
A. Myth-busting: Popular Beliefs vs. Scientific Evidence
Myth: All Bacteria Are Harmful: Contrary to the misconception that all bacteria are harmful, the gut is home to a vast community of beneficial bacteria that play crucial roles in digestion, nutrient absorption, and supporting the immune system. Understanding the distinction between harmful and beneficial bacteria is essential for promoting a balanced gut microbiome.
Myth: Probiotics Alone Are Sufficient: While probiotics contribute to gut health, relying solely on supplements may not address the complex nature of the gut microbiome. A diverse and fiber-rich diet, along with prebiotics that nourish existing bacteria, is equally important for fostering a resilient and thriving gut environment.
B. Understanding the Complexity of Gut Health
Individualized Nature of Gut Health: Gut health is highly individualized, influenced by genetics, lifestyle, and environmental factors. What works for one person may not be suitable for another. Tailoring dietary and lifestyle choices to individual needs and responses is key to optimizing gut health.
Long-Term Commitment to Gut Health: Achieving and maintaining optimal gut health is not a quick fix but rather a long-term commitment. Consistent, positive dietary and lifestyle choices contribute to the sustainability of a healthy gut microbiome, emphasizing the importance of ongoing efforts.
Gut Health Extends Beyond Digestion: While the gut is central to digestion, its influence extends beyond the digestive system. The gut-brain axis underscores the connection between gut health and mental well-being, emphasizing the holistic impact of a healthy gut on overall health.
Dispelling these common misconceptions allows individuals to approach gut health with a more informed and nuanced perspective. Acknowledging the complexity of the gut microbiome and understanding the need for a holistic, individualized approach empowers individuals to make choices that support long-term gut health and overall well-being.
In the concluding section, we will recap key insights from each section, encouraging readers to embrace a comprehensive approach to health that prioritizes the intricate relationship between gut health and nutrient absorption.

A. Recap of Key Points
Gut Health Fundamentals: We began by defining gut health and highlighting its fundamental role in overall well-being. Understanding the importance of nutrient absorption within the digestive process laid the groundwork for exploring strategies to maximize the benefits of a balanced diet.
The Gut Microbiome’s Crucial Role: Delving into the gut microbiome emphasized the dynamic nature of this ecosystem and its impact on digestion, nutrient absorption, and various aspects of health. Recognizing the influence of factors such as diet, lifestyle, and stress on the microbiome highlighted the interconnectedness of these elements.
Influencing Factors and Signs of Poor Gut Health: Section III explored dietary choices, lifestyle habits, and the avoidance of harmful substances as influential factors in gut health. Recognizing signs of poor gut health, including digestive issues and nutrient deficiencies, provided valuable insights for self-assessment.
Strategies for Improvement: Section V detailed practical approaches to enhance gut health, emphasizing the importance of dietary choices, lifestyle modifications, and adequate hydration. The holistic nature of these strategies reflected the multifaceted impact of our decisions on gut well-being.
Maximizing Nutrient Absorption: Section VI focused on optimizing nutrient absorption through mindful food combinations, cooking techniques, and strategic meal timing. These insights provided actionable steps for individuals seeking to extract the maximum nutritional value from their diets.
Dispelling Misconceptions: Section VII addressed common misconceptions, debunking myths about bacteria, probiotics, and the simplistic nature of gut health. Emphasizing the individualized and complex aspects of gut health provided a more nuanced understanding for readers.
B. Encouraging a Holistic Approach to Health
Long-Term Commitment: Achieving and maintaining optimal gut health is a journey that requires a long-term commitment. Consistent, positive choices contribute to the sustainability of a healthy gut microbiome, underscoring the importance of ongoing efforts.
Mind-Body Connection: The gut-brain axis serves as a reminder of the interconnectedness between gut health and mental well-being. Nurturing the gut extends beyond physical health, influencing aspects of cognition, mood, and overall vitality.
Empowering Individuals: Armed with knowledge about gut health and nutrient absorption, individuals are empowered to make informed choices. Recognizing the uniqueness of each person’s physiology allows for personalized approaches that align with individual needs and preferences.
In conclusion, prioritizing gut health and optimizing nutrient absorption is a holistic endeavor that goes beyond conventional dietary advice. By embracing the interconnectedness of lifestyle choices, microbiome health, and overall well-being, individuals can embark on a journey toward a healthier, more vibrant life. As we continue to unravel the complexities of the gut, staying informed and adopting evidence-based practices will be essential for promoting a balanced and thriving digestive system.

What you eat directly impacts your digestion, bowel movements, and overall gut health. Struggling with constipation, bloating, or irregularity? The key lies in your diet.

You’ve been pooping wrong your entire life—and it’s wrecking your gut. Dr. Gina Sam’s poop method reveals the shockingly simple, doctor-backed fix that makes straining
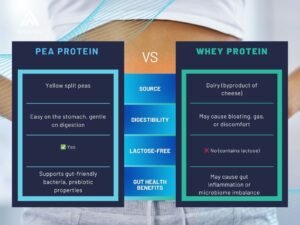
Struggling with bloating after protein shakes? Your choice of protein could be affecting your gut health. Pea protein is gentle and gut-friendly, while whey protein

Table of Contents <svg aria-hidden=”true” viewBox=”0 0 448 512″ xmlns=”http://www.w3.org/2000/svg”><path d=”M207.029 381.476L12.686 187.132c-9.373-9.373-9.373-24.569 0-33.941l22.667-22.667c9.357-9.357 24.522-9.375 33.901-.04L224 284.505l154.745-154.021c9.379-9.335 24.544-9.317 33.901.04l22.667 22.667c9.373 9.373 9.373 24.569 0 33.941L240.971

Happy Poops.
What about your friends?